Science:MMA与nBA共聚物自愈合材料重大进展
研究人员发现非常普通的自愈合共聚物材料:
甲基丙烯酸甲酯与丙烯酸正丁酯两种单体在一个非常窄的比例范围内(Molar% MMA/nBA=45/55 to 55/55)进行共聚到的共聚物薄膜在室温下具有自愈合性能,两种共聚单体的比例高于或低于这个比例均无自愈合能力,而且这种自愈合能力仅仅靠范德华力。
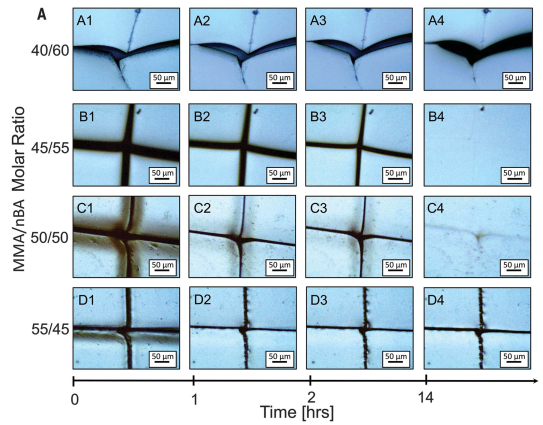
以上内容仅供参考学习。
参考文献:
Key-and-lock commodity self-healing copolymers.Marek W. Urban1,2,3,*, Dmitriy Davydovich1,3, Ying Yang1,3, Tugba Demir1,3, Yunzhi Zhang2, Leah Casabianca2
See all authors and affiliations
Science 12 Oct 2018:
Vol. 362, Issue 6411, pp. 220-225
DOI: 10.1126/science.aat2975
Abstract
Self-healing materials are notable for their ability to recover from physical or chemical damage. We report that commodity copolymers, such as poly(methyl methacrylate)/n-butyl acrylate [p(MMA/nBA)] and their derivatives, can self-heal upon mechanical damage. This behavior occurs in a narrow compositional range for copolymer topologies that are preferentially alternating with a random component (alternating/random) and is attributed to favorable interchain van der Waals forces forming key-and-lock interchain junctions. The use of van der Waals forces instead of supramolecular or covalent rebonding or encapsulated reactants eliminates chemical and physical alterations and enables multiple recovery upon mechanical damage without external intervention. Unlike other self-healing approaches, perturbation of ubiquitous van der Waals forces upon mechanical damage is energetically unfavorable for interdigitated alternating/random copolymer motifs that facilitate self-healing under ambient conditions.