温敏聚合物PolyNiPAM派上用场:当士兵遭遇战争可能损伤眼睛,玻璃体溢出可能导致视网膜脱落,如果得不到及时的救治,可能导致失明。南加州大学研究人员开发一种热可逆凝胶用于快速救治伤员阻止玻璃体泄露和视网膜脱落。
使用的聚合物材料即聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺【Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)】,简称PolyNiPAm,结构如下图:
在室温下这种材料对眼睛无粘附性,当与眼睛接触达到体温时,PolyNiPAm材料迅速变粘,可以密封伤口使眼球内的玻璃体和体液不泄露。基于PolyNiPAM的材料随温度变化的粘附性质如下图:
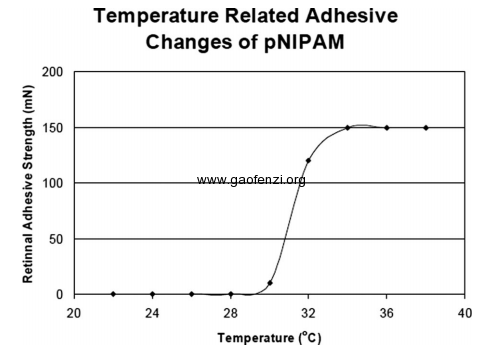
所以当士兵眼部受伤时,利用这种材料进行密封,当达到医院时,可以通过降温使材料无粘附性从而轻易取出密封材料,再进行治疗。通过在猪上进行的实验,充分说明了这种材料的依赖温度粘附的可逆性。研究人员在2014年眼科视觉年会上介绍了他们的这项研究成果(2014 Annual Meeting of the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) )。
想要详细研究这种保护眼睛的可逆胶材料,可以参考如下文献:
文献:Retina. 2007 Sep;27(7):938-42.
标题:Reversible thermosensitive glue for retinal implants
作者:Tunc M1, Cheng X, Ratner BD, Meng E, Humayun M.
摘要:
PURPOSE:
To determine in vitro effects of a plasma polymerized N-isopropyl acrylamide (pNIPAM) coating for thermally controllable adhesion to retinal tissue.
RESULTS:
There was no retinal adhesion at room temperature (22 degrees C). The adhesion developed strongly within 60 seconds after reaching the critical temperature (>or=32 degrees C). This adhesion was persistent when the authors applied tractional forces of 98 mN and 148 mN between 32 and 38 degrees C. When the authors lowered the temperature back to 22 degrees C by irrigation with cold BSS, the implants detached from the retinal surface without using any tractional force.
CONCLUSION:
pNIPAM provides effective in vitro retinal adhesion between 32 and 38 degrees C and this adhesion is completely reversible by lowering the temperature of the physiologic medium.
